Canine Health News You Can Use
In June, Virbac recalled VeggieDent Chews for Dogs in Australia as a precautionary measure after veterinary researchers noticed a possible link between dogs developing kidney disease and consumption of these chews. No reason has been found and there is as yet no proof that the chews are causing the Fanconi-like syndrome. The chews were introduced to Australia in March of this year. They are manufactured in Vietnam, and are made of corn, starch, glycerin, soy, rice, yeast, sorbitol, corn derivatives, and water. VeggieDent chews have been marketed in the U.S. since September 2008, and in Europe and Japan for two years, but Virbac claims it has not received reports of problems anywhere except Australia – the only country that required some imported pet foods to be irradiated. Virbac blames the irradiation for the problem.
Hemorrhagic Gastroenteritis in Dogs
The symptoms came on fast and furious. One day Chloe was a healthy, tail-wagging Labrador Retriever and the next day she was vomiting mucus all over the house. Then her vomit turned red with blood and then came matching diarrhea. Chloe had hemorrhagic gastroenteritis, or HGE. Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis is a mystery disease. No one knows what causes it and there is no recommended prevention. It does not seem to be contagious from one dog to another, although dogs living together sometimes develop HGE at the same time, and some parts of the country have reported outbreaks of several cases. It's most dangerous for small dogs, and although some veterinarians consider toy and miniature breeds between the ages of two and four the most typical HGE patients, males and females of all breeds and ages have been affected. There are few, if any, HGE warning signs. It is not usually accompanied by a fever. Diarrhea containing bright or dark red blood is the illness's signature symptom. Vomiting, which usually accompanies the diarrhea, typically begins as mucus or bile and then becomes bloody. Affected dogs may eat grass and vomit that as well.
Probiotics and Dogs
Curly, a five-year-old Standard Poodle, eats the best food his human can afford. Raw chicken, rabbit, and venison are his favorites. Tina, his two-legged companion, switches the meats every few days, mixing the protein with some sweet potato, carrots, an occasional stalk of broccoli, and always a good fish oil supplement. Plus, to be sure that Curly is getting full nutritional benefit from every delicious bite, Tina always adds a sprinkling of a probiotic and digestive enzyme supplement as a final touch. Everything Curly eats is the best of the best: human-grade ingredients, no preservatives, no by-products. But somehow, despite all of the good lovin' and great food, Curly is a bit thin, won't put on weight, and his stool is sometimes dry making it hard for the poor guy to poop during his daily walks. Tina knows that something is amiss and she is worried. She was told that maybe the probiotics weren't active, so she tried several different brands. But nothing has improved. So what gives; is it that the probiotics don't work? Adding supplemental Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Lactobacillus bulgaricus, or other probiotic organisms to your dog's diet is almost always a good idea. This will support the resident microflora that are always present in Curly's gut, enhancing digestion and absorption of nutrients, supporting detoxification and elimination processes, and helping to boost his immune system.
Canine Swimming Lessons: The Perfect Exercise For Your Dog
For those of us who regularly swim for fitness, we know why swimming is often referred to as “the perfect exercise.” In addition to the physical benefits shared with other forms of aerobic exercise, swimming offers some unique benefits. It eliminates the effects of weight-bearing on the joints, exercises the entire body – upper and lower – at the same time, and, in most cases, is something we can do for our entire lives, even if age precludes us from taking part in other forms of exercise. The physical benefits of swimming are the same for your canine companion as they are for you – that is, if you have a dog who will swim. Even though they actually have a stroke named after them, the notion that all dogs are “natural swimmers” is an erroneous one. Some breeds were developed to work in water and are more physically adapted for swimming than others. The problem here is not getting these dogs into the water, but keeping them on terra firma when we want them to stay clean and dry. However, occasionally, even a water breed shows disdain for water – yes, there are some Labrador Retrievers who hate swimming. Conversely, there are dogs you’d never imagine taking kindly to the water who become devoted and skilled swimmers. Although not blessed with the physical advantages of a water breed, and despite sinking rear ends or heavy, wet coats, these Boston Terriers, Rhodesian Ridgebacks, and Siberian Huskies have learned to enjoy swimming. They don’t know or care that they have to work a little harder than a Poodle, Cocker Spaniel, or a Newfoundland – they just want to have fun!
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency in Dogs
Kanis Fitzhugh, a member of the Almost Home organization, knew she had to rescue Pandy, an extremely thin and seemingly vicious four-year-old Dachshund. Pandy had been relinquished to a shelter in Orange County (California), who turned her over to Southern California Dachshund Rescue. Deemed people- and animal-aggressive, Pandy appeared to have been starved, and weighed just 13 pounds. Fitzhugh thought the dog deserved a break, and brought Pandy home in May 2007. During the first couple of weeks in her new home, Pandy managed to pull a chicken down from the counter and proceeded to eat the entire bird, including bones, plastic tray, and grocery bag, in less than the 10 minutes that Fitzhugh was out of the room. Pandy was rushed to the vet and emergency surgery was performed, as the bones had ruptured her stomach lining in three places. Luckily, she survived. Pandy's voracious appetite, large voluminous stools, and aggressive disposition were all caused by a medical condition called exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI). With Fitzhugh's loving care, including enzyme supplements and a change of diet, Pandy stabilized. Within a year, Pandy had transformed into a beautiful, funny, 26-pound Dachshund who gets along great with all the human and animal members in the Fitzhugh household. Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency, or EPI, also referred to as Pancreatic Hypoplasia or Pancreatic Acinar Atrophy (PAA), is a disease of maldigestion and malabsorption, which when left untreated eventually leads to starvation. One of the major difficulties with this disease is in the prompt and accurate diagnosis. Astonishingly, visible symptoms may not appear until 80 to 95 percent of the pancreas has atrophied.
Healthy Low-Fat Diets For Dogs With Special Dietary Needs
Some low-fat recipes for dogs are excessively low in fat, providing as little as 5 to 8 GFK, with as much as seven times more starches than meat. With very few exceptions, its not necessary to feed such an extremely low-fat diet to dogs recovering from or prone to pancreatitis or with other forms of fat intolerance, nor is such a diet likely to be nutritionally adequate, regardless of how many supplements you add.
Canine Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis literally means inflammation of the pancreas, the glandular organ that secretes enzymes needed to digest food. When something causes these enzymes to be activated prematurely, they can actually begin to digest the pancreas itself, resulting in pain and inflammation. Pancreatitis occurs in two different forms, acute and chronic, and both may be either mild or severe. Acute pancreatitis occurs suddenly and is more often severe, while chronic pancreatitis refers to an ongoing inflammation that is usually less severe and may even be subclinical (no recognizable symptoms). Acute pancreatitis can be extremely painful, and can become life-threatening if the inflammation spreads, affecting multiple organs and systems. Symptoms commonly include anorexia (loss of appetite), vomiting, weakness, depression, and abdominal pain. Abdominal pain in a dog may be exhibited as restlessness or not wanting to move; a hunched appearance or a praying position, with the chest down and the rear raised; or vocalization (crying or whimpering). Additional symptoms may include diarrhea, drooling, fever, and collapse.
Kennel Cough Treatment and Prevention
Anyone who's heard it will recognize the dry, hacking, something's-stuck-in-my-throat cough that won't quit. It's the signature symptom of canine infectious tracheobronchitis, also known as Bordetellosis, Bordetella, and most commonly as kennel cough. Whatever you call it, tracheobronchitis is one of the world's most widespread canine diseases. Like the common cold in humans, tracheobronchitis is highly contagious, rarely fatal, and runs its course in a few days. Fortunately, there are several ways to help make canine patients more comfortable, speed recovery, and prevent future infections. Tracheobronchitis is called kennel cough because of its association with boarding kennels, animal shelters, veterinary waiting rooms, grooming salons, and other areas where dogs congregate in close quarters. It can strike dogs of any age but is most common in puppies, whose immune systems are still developing, and adult dogs with conditions that impair immune function.
Dog Vaccination Information
Vaccines are something that every dog owner should be educated about, and yet few seem to think about them at all, except to wonder about the need for them after they get a new dog. However, many people base this concern on the vet bill, rather than worries about the potential for side effects in their dogs! Immunology expert Ronald Schultz, PhD, Diplomate ACVIM (American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine), has spent much of his career studying animal vaccines. Dr. Schultz is professor and chair of the Department of Pathobiological Sciences at the University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Veterinary Medicine, and has more than 40 years' experience in the field of immunology. His long-time university employment - as opposed to a career in industry - has provided him with a unique position of neutrality from which to observe the vaccine industry.
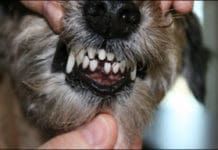
Fractured Teeth in Dogs
Between runs at a recent agility competition, I was chatting with Katie and Nora, a couple of handlers I often see at trials. Coincidentally, all three of our dogs had received an annual health examination from our respective general practice veterinarians recently, with all dogs earning good reports. And all three of us had been told by our veterinarians that our dogs had broken or chipped teeth. My veterinarian had noted a slab fracture of the upper fourth premolar" on the health summary report for my 10-year-old Border Terrier
Canine Vestibular Disease
the cerebellum and brain stem
Shock Wave Therapy For Dogs With Arthritis
but after only one eSWT treatment